Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following diatomic molecules is joined by a double covalent
bond?
|
|
|
2.
|
What type of hybridization occurs in the orbitals of a carbon atom participating
in a triple bond with another carbon atom?
|
|
|
3.
|
What is thought to cause the dispersion forces?
a. | attraction between ions | c. | sharing of electron
pairs | b. | motion of electrons | d. | differences in electronegativity |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest?
a. | dipole interaction | c. | hydrogen bond | b. | dispersion | d. | single covalent
bond |
|
|
|
5.
|
Why are the molecules of hydrocarbons nonpolar?
a. | The intermolecular attractions are strong. | b. | All the bonds are
single covalent bonds. | c. | The electron pair is shared almost equally in
all the bonds. | d. | Van der Waals forces overcome polarity. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following compounds is an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
a. | methane | c. | nonane | b. | propyne | d. | methyl |
|
|
|
7.
|
A structural isomer of hexane is ____.
a. | 2,2-dimethylbutane | c. | benzene | b. | cyclohexane | d. | 2-methylpentene |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following molecules does NOT display resonance?
a. | benzene | c. | m-xylene | b. | phenylethane | d. | cyclohexane |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which carbon skeleton represents an ester?
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the expected product when l-propanol is oxidized?
a. | propanal | c. | propanoic acid | b. | propanone | d. | propene |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following bonds is the least reactive?
|
|
|
12.
|
How is a pair of molecular orbitals formed?
a. | by the splitting of a single atomic orbital | b. | by the reproduction
of a single atomic orbital | c. | by the overlap of two atomic orbitals from the
same atom | d. | by the overlap of two atomic orbitals from different
atoms |
|
|
|
13.
|
What causes water molecules to have a bent shape, according to VSEPR
theory?
a. | repulsive forces between unshared pairs of electrons | b. | interaction between
the fixed orbitals of the unshared pairs of oxygen | c. | ionic attraction and
repulsion | d. | the unusual location of the free electrons |
|
|
|
14.
|
Experimental evidence suggests that the H—C—H bond angles in ethene,
C 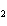 H 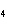 , are
____.
|
|
|
15.
|
What causes dipole interactions?
a. | sharing of electron pairs | b. | attraction between polar
molecules | c. | bonding of a covalently bonded hydrogen to an unshared electron
pair | d. | attraction between ions |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which type of solid has the highest melting point?
a. | ionic solid | c. | metal | b. | network solid | d. | nonmetallic
solid |
|
|
|
17.
|
How many carbons are in a molecule of hexane?
|
|
|
18.
|
What is the physical state of the smallest alkanes at room temperature?
a. | gas | c. | solid | b. | liquid | d. | gas or liquid |
|
|
|
19.
|
In which of the following compounds does rotation occur around all covalent
bonds between carbons?
a. | octene | c. | octane | b. | octyne | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following compounds is a structural isomer of butane?
a. | 2-methylbutane | c. | 2-methylpropane | b. | 2,2-dimethylbutane | d. | 2,2-diethylpropane |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following is true about structural isomers?
a. | Structural isomers have the same molecular formula. | b. | Structural isomers
have different physical and chemical properties. | c. | Structural isomers have the same elemental
composition. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following is NOT an important fossil fuel?
a. | petroleum | c. | natural gas | b. | hydrogen | d. | coal |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the carbon skeleton of the product formed in the following reaction?
C 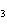 H 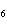 + HBr → a. |
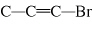 | c. |
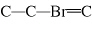 | b. |
CCCBr | d. |
CCBrC |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following alcohols is used in antifreeze?
a. | ethanol | c. | ethylene glycol | b. | isopropyl alcohol | d. | glycerol |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
25.
|
Write the general structure for ester compounds.
|
|
|
26.
|
Write the general structure for carboxylic acid compounds.
|
Essay
|
|
|
27.
|
What are dispersion forces? How is the strength of dispersion forces related to
the number of electrons in a molecule? Give an example of molecules that are attracted to each other
by dispersion forces.
|
|
|
28.
|
Compare the properties of the alcohols with the properties of the halocarbons
and the alkanes.
|