Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
How many double covalent bonds are in an alkane?
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the simplest straight-chain alkane?
a. | graphite | c. | methane | b. | ammonia | d. | ethane |
|
|
|
3.
|
The names of the straight-chain alkanes all end with the suffix ____.
|
|
|
4.
|
The condensed structural formula for 2,2,3-trimethylbutane is ____.
|
|
|
5.
|
Why are the molecules of hydrocarbons nonpolar?
a. | The intermolecular attractions are strong. | b. | All the bonds are
single covalent bonds. | c. | The electron pair is shared almost equally in
all the bonds. | d. | Van der Waals forces overcome polarity. |
|
|
|
6.
|
The general name for hydrocarbons with at least one triple covalent bond is
____.
a. | alkenes | c. | alkanes | b. | alkyls | d. | alkynes |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is true about structural isomers?
a. | Structural isomers have the same molecular formula. | b. | Structural isomers
have different physical and chemical properties. | c. | Structural isomers have the same elemental
composition. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
8.
|
In the cis configuration, the methyl groups are placed ____.
a. | in between the double bonds | c. | to the left of the double
bond | b. | on opposite sides of the double bond | d. | on the same side of the double
bond |
|
|
|
9.
|
Hydrocarbons containing a saturated carbon ring are called ____.
a. | cyclic hydrocarbons | c. | aliphatic hydrocarbons | b. | aromatic
hydrocarbons | d. | alkylated
hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the first step in the refining of petroleum?
a. | cracking | c. | cooling | b. | drilling | d. | distillation |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following is NOT a product obtained from the distillation of coal
tar?
a. | benzene | c. | coke | b. | phenol | d. | toluene |
|
|
|
12.
|
The most important way to classify organic compounds is by ____.
a. | the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain | b. | functional
group | c. | the type of carbon—carbon bonds | d. | reactivity |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which halocarbon has the highest boiling point?
a. | 1-chloropropane | c. | 1,2,3-trichloropropane | b. | 2-chloropropane | d. | 2-dichloropropane |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following compounds is trichloromethane?
|
|
|
15.
|
An example of a secondary alcohol is shown by the structure ____.
|
|
|
16.
|
Phenols are characterized by ____.
a. | their behavior as gases | c. | an OH group on a benzene ring | b. | ether
linkages | d. | their use as
flavoring agents |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the common name of the following alcohol? 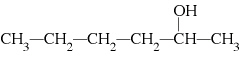 a. | sec-hexyl alcohol | c. | isohexyl
alcohol | b. | tert-hexyl alcohol | d. | hexyl alcohol |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following alcohols is used in antifreeze?
a. | ethanol | c. | ethylene glycol | b. | isopropyl alcohol | d. | glycerol |
|
|
|
19.
|
In an addition reaction, which bond of the reactant is broken?
a. | carbon—carbon single bond | c. | carbon—carbon double
bond | b. | carbon—hydrogen single bond | d. | carbon—hydrogen double
bond |
|
|
|
20.
|
The functional group in CH 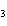 O CH 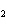 CH 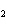 CH 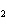 CH 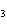 is a(n)
____. a. | ester | c. | carbonyl | b. | ether | d. | carboxyl |
|
|
|
21.
|
Name the compound CH 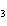 CH 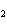 O CH 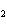 CH 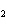 CH 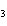 . a. | diethyl ether | c. | ethylpropyl ether | b. | dipropyl ether | d. | pentane oxide |
|
|
|
22.
|
What type of compound is the following? 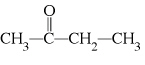 a. | alcohol | c. | ether | b. | aldehyde | d. | ketone |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which carbon skeleton represents an aldehyde?
a. |
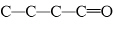
| c. |
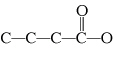 | b. |
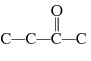 | d. |
none of the
above |
|
|
|
24.
|
Aldehydes have the general structure ____________.
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
a. | 2-pentanone | c. | pentene | b. | pentane | d. | chloropentane |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following compounds is known as acetic acid?
|
|
|
27.
|
The IUPAC name for a carboxylic acid with two carbons in a straight chain would
be ____.
a. | ethanalic acid | c. | methacarboxylic acid | b. | dimethylmethanoic acid | d. | ethanoic acid |
|
|
|
28.
|
Esters contribute which property to fruits?
a. | odor | c. | texture | b. | color | d. | skin thickness |
|
|
|
29.
|
If a primary alcohol is oxidized, the type of molecule it becomes is called a(n)
____.
a. | carboxylic acid | c. | alcohol | b. | ketone | d. | aldehyde |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following compounds will produce the least energy when completely
oxidized?
a. | hexanoic acid | c. | hexane | b. | hexanol | d. | hexanal |
|
|
|
31.
|
The monomer used as the building block in polyethylene is ____.
a. | ethane | c. | monoethane | b. | ethene | d. | amino acid |
|
|
|
32.
|
What happens in a condensation reaction?
a. | head-to-tail joining of monomers | b. | side-by-side joining of
monomers | c. | cross-linking of monomers | d. | substitution of a halogen on
monomers |
|
|
|
33.
|
The simple sugars are also called ____.
a. | alcohols | c. | cycloalkanes | b. | carboxylic acids | d. | monosaccharides |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which form of polysaccharide is found in animals?
a. | starch | c. | sucrose | b. | glycogen | d. | glucose |
|
|
|
35.
|
The repeating unit of cellulose is ____.
a. | glucose | c. | fructose | b. | lactose | d. | sucrose |
|
|
|
36.
|
A peptide bond is a bond between which functional groups?
a. | amino and alcohol | c. | carboxyl and alcohol | b. | amino and carboxyl | d. | carbonyl and
carbonyl |
|
|
|
37.
|
Saponification is what type of reaction?
a. | hydrolysis | c. | hydrogenation | b. | dehydrogenation | d. | acid-base |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
38.
|
How many more hydrogen atoms does a cyclohexane molecule have than a benzene
molecule?
|
|
|
39.
|
Write complete, balanced equations for the reaction of 2-pentene and water. Use
structural formulas.
|
|
|
40.
|
What is the expected product when the following compound is oxidized? CH 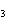 CH 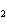 CH 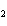 CH 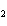 OH
|
Essay
|
|
|
41.
|
Describe the arrangement of atoms in ethyne. What is the significance of this
arrangement?
|
|
|
42.
|
Explain how geometric isomers differ from each other. Describe the difference
between the trans and cis configurations of geometric isomers. Provide an example of
each configuration for a molecule that has geometric isomers.
|
|
|
43.
|
Compare the properties of the aldehydes and ketones with the properties of
alcohols, ethers, alkanes, and halocarbons.
|
|
|
44.
|
Describe the process of making soap.
|