Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element
is a(n) ____.
a. | atom | c. | proton | b. | electron | d. | neutron |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following is NOT a part of Dalton's atomic theory?
a. | All elements are composed of atoms. | b. | Atoms are always in motion. | c. | Atoms of the same
element are identical. | d. | Atoms that combine do so in simple whole-number
ratios. |
|
|
|
3.
|
The comparison of the number of atoms in a copper coin the size of a penny with
the number of people on Earth is made to illustrate which of the following?
a. | that atoms are indivisible | b. | that atoms are very small | c. | that atoms are very
large | d. | that in a copper penny, there is one atom for every person on
Earth |
|
|
|
4.
|
Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all
elements?
a. | Cathode rays are negatively-charged particles. | b. | Cathode rays can be
deflected by magnets. | c. | An electron is 2000 times lighter than a
hydrogen atom. | d. | Charge-to-mass ratio of electrons was the same, regardless of the gas
used. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom are ____.
a. | neutrons and electrons | c. | protons and neutrons | b. | electrons only | d. | protons and
electrons |
|
|
|
6.
|
The nucleus of an atom is ____.
a. | the central core and is composed of protons and neutrons | b. | positively charged
and has more protons than neutrons | c. | negatively charged and has a high
density | d. | negatively charged and has a low density |
|
|
|
7.
|
An element has an atomic number of 76. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 152 protons and 76 electrons | c. | 38 protons and 38
electrons | b. | 76 protons and 0 electrons | d. | 76 protons and 76 electrons |
|
|
|
8.
|
Isotopes of the same element have different ____.
a. | positions on the periodic table | c. | atomic numbers | b. | chemical
behavior | d. | mass
numbers |
|
|
|
9.
|
If E is the symbol for an element, which two of the following symbols represent
isotopes of the same element? a. | 1 and 2 | c. | 1 and 4 | b. | 3 and 4 | d. | 2 and 3 |
|
|
|
10.
|
The atomic mass of an element is the ____.
a. | total number of subatomic particles in its nucleus | b. | weighted average of
the masses of the isotopes of the element | c. | total mass of the isotopes of the
element | d. | average of the mass number and the atomic number for the
element |
|
|
|
11.
|
In the Bohr model of the atom, an electron in an orbit has a fixed ____.
a. | position | c. | energy | b. | color | d. | size |
|
|
|
12.
|
How many energy sublevels are in the second principal energy level?
|
|
|
13.
|
What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy
level?
|
|
|
14.
|
The shape (not the size) of an electron cloud is determined by the
electron's ____.
a. | energy sublevel | c. | speed | b. | position | d. | principal quantum
number |
|
|
|
15.
|
According to the aufbau principle, ____.
a. | an orbital may be occupied by only two electrons | b. | electrons in the
same orbital must have opposite spins | c. | electrons enter orbitals of highest energy
first | d. | electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first |
|
|
|
16.
|
How many unpaired electrons are in a sulfur atom (atomic number 16)?
|
|
|
17.
|
How does the speed of visible light compare with the speed of gamma rays, when
both speeds are measured in a vacuum?
a. | The speed of visible light is greater. | b. | The speed of gamma rays is
greater. | c. | The speeds are the same. | d. | No answer can be determined from the
information given. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The light given off by an electric discharge through sodium vapor is
____.
a. | a continuous spectrum | c. | of a single wavelength | b. | an emission
spectrum | d. | white
light |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the approximate energy of a photon having a frequency of 4 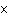
10 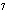 Hz? ( h = 6.6 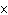 10 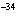 J  s)
|
|
|
20.
|
Which variable is directly proportional to frequency?
a. | wavelength | c. | position | b. | velocity | d. | energy |
|
|
|
21.
|
What are quanta of light called?
a. | charms | c. | muons | b. | excitons | d. | photons |
|
|
|
22.
|
The quantum mechanical model of the atom ____.
a. | defines the exact path of an electron around the nucleus | b. | was proposed by
Niels Bohr | c. | involves the probability of finding an electron in a certain
position | d. | has many analogies in the visible world |
|
|
|
23.
|
According to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, if the position of a moving
particle is known, what other quantity CANNOT be known?
a. | mass | c. | spin | b. | charge | d. | velocity |
|
Numeric Response
|
|
|
24.
|
How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of a neutral
chlorine atom?
|