Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
What would likely happen if you were to touch the flask in which an endothermic
reaction were occurring?
a. | The flask would probably feel cooler than before the reaction
started. | b. | The flask would probably feel warmer than before the reaction
started. | c. | The flask would feel the same as before the reaction started. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following is NOT a form of energy?
a. | light | c. | heat | b. | pressure | d. | electricity |
|
|
|
3.
|
If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat will be
____.
a. | absorbed by the surroundings | c. | released by the
surroundings | b. | absorbed by the universe | d. | released by the universe |
|
|
|
4.
|
In an exothermic reaction, the energy stored in the chemical bonds of the
reactants is ____.
a. | equal to the energy stored in the bonds of the products | b. | greater than the
energy stored in the bonds of the products | c. | less than the energy stored in the bonds of the
products | d. | less than the heat released |
|
|
|
5.
|
What is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 200.0 g of
aluminum by 10 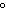 C? (specific heat of aluminum = 0.21 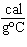 ) a. | 420 cal | c. | 42,000 cal | b. | 4200 cal | d. | 420,000 cal |
|
|
|
6.
|
How many kilocalories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 225 g of
aluminum from 20 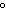 C to 100 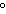 C? (specific
heat of aluminum = 0.21 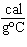 ) a. | 0.59 kcal | c. | 85 kcal | b. | 3.8 kcal | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
7.
|
When 45 g of an alloy, at 25 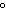 C, are dropped into 100.0 g
of water, the alloy absorbs 956 J of heat. If the final temperature of the alloy is 37 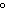 C,
what is its specific heat? a. | 0.423 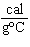 | c. | 9.88 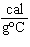 | b. | 1.77 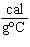 | d. | 48.8 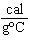 |
|
|
|
8.
|
How can you describe the specific heat of olive oil if it takes approximately
420 J of heat to raise the temperature of 7 g of olive oil by 30  C? a. | greater than the specific heat of water | c. | equal to the specific heat of
water | b. | less than the specific heat of water | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Standard conditions of temperature and pressure for a thermochemical equation
are ____.
a. | 0 C and 101 kPa C and 101 kPa | c. | 0 C and 0
kPa C and 0
kPa | b. | 25 C and 101 kPa C and 101 kPa | d. | 25 C and 22.4
kPa C and 22.4
kPa |
|
|
|
10.
|
The specific heat of silver is 0.24 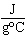 . How many joules of energy
are needed to warm 4.37 g of silver from 25.0  C to 27.5  C? a. | 2.62 J | c. | 45.5 J | b. | 0.14 J | d. | 0.022 J |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following has the greatest heat capacity?
a. | 1000 g of water | c. | 1 g of water | b. | 1000 g of steel | d. | 1 g of steel |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following substances has the highest specific heat?
a. | steel | c. | alcohol | b. | water | d. | chloroform |
|
|
|
13.
|
The amount of heat transferred from an object depends on which of the
following?
a. | the specific heat of the object | c. | the mass of the
object | b. | the initial temperature of the object | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
14.
|
On what principle does calorimetry depend?
a. | Hess's law | c. | law of enthalpy | b. | law of conservation of
energy | d. | law of multiple
proportions |
|
|
|
15.
|
A chunk of ice whose temperature is –20  C is added to
an insulated cup filled with water at 0  C. What happens in the cup? a. | The ice melts until it reaches the temperature of the water. | b. | The water cools
until it reaches the temperature of the ice. | c. | Some of the water freezes, so the chunk of ice
gets larger. | d. | none of the above |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the standard heat of reaction for the following
reaction? Zn( s) + Cu 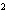 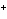 ( aq) 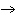 Zn 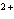 ( aq) +
Cu( s) (  H H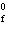 for Cu 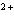 =
+64.4 kJ/mol;  H H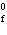 for Zn 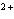
= –152.4 kJ/mol) a. | 216.8 kJ released per mole | c. | 88.0 kJ absorbed per
mole | b. | 88.0 kJ released per mole | d. | 216.8 kJ absorbed per mole |
|
|
|
17.
|
Calculate  H H for the following reaction. C 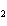 H 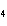 ( g) + H 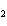 ( g)
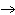 C 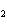 H 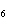 ( g) (  H H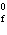 for C 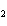 H 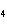 ( g) = 52.5 kJ/mol;  H H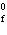 for C 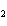 H 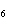 ( g) = –84.7 kJ/mol) a. | –137.2 kJ | c. | 32.2 kJ | b. | –32.2 kJ | d. | 137.2 kJ |
|
|
|
18.
|
Calculate the energy released when 24.8 g Na 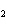 O reacts in
the following reaction. Na 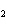 O( s) + 2HI( g)  2NaI( s) + H 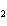 O( l)  H H = –120.00 kcal a. | 0.207 kcal | c. | 48.0 kcal | b. | 2.42 kcal | d. | 3.00 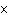 10 10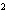 kcal
kcal |
|
|
|
19.
|
To calculate the amount of heat absorbed as a substance melts, which of the
following information is NOT needed?
a. | the mass of the substance | c. | the change in
temperature | b. | the specific heat of the substance | d. | the density of the
sample |
|
|
|
20.
|
The  H H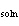 is
____. a. | always negative | b. | always positive | c. | sometimes positive,
sometimes negative | d. | always 0 |
|
|
|
21.
|
When 1.0 g of solid NaOH (  H H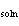 =
–445.1 kJ/mol) dissolves in 10 L of water, how much heat is released? a. | 445.1 kJ | c. | 11.1 J | b. | 405.1 kJ | d. | 11.1 kJ |
|
|
|
22.
|
When 10 g of diethyl ether is converted to vapor at its boiling point, about how
much heat is absorbed? (C 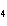 H 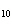 O,  H H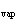 = 15.7 kJ/mol, boiling point: 34.6 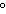 C) a. | 2 kJ | c. | 0.2 kJ | b. | 2 J | d. | Not enough information is
given. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Hess's law ____.
a. | makes it possible to calculate  H for complicated
chemical reactions H for complicated
chemical reactions | b. | states that when you reverse a chemical
equation, you must change the sign of  H H | c. | determines the way a
calorimeter works | d. | describes the vaporization of
solids |
|
|
|
24.
|
 H H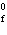 for the formation of
rust (Fe 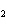 O 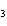 ) is –826 kJ/mol. How
much energy is involved in the formation of 5 grams of rust? a. | 25.9 kJ | c. | 66 kJ | b. | 25.9 J | d. | 66 J |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
25.
|
The specific heat capacity of graphite is 0.71 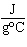 . Calculate
the energy required to raise the temperature of 750 g of graphite by 160 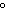 C.
|
|
|
26.
|
Suppose a substance has a heat of fusion equal to 45 cal/g and a specific heat
of 0.75 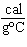 in the liquid state. If 5.0 kcal of heat are
applied to a 50-g sample of the substance at a temperature of 24 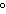 C, what will
its new temperature be? What state will the sample be in? (melting point of the substance = 27 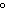 C; specific heat of the solid = 0.48 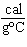 ; boiling point of the
substance = 700 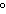 C)
|
|
|
27.
|
Consider a 67-g chunk of ice (  H H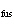 =
6.0 kJ/mol) in a beaker immersed in a water bath. To produce just enough heat to melt the ice, how
many moles of solid NaOH (  H H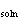 =
–445.1 kJ/mol) must you dissolve in the water bath?
|
|
|
28.
|
|
|
|
29.
|
A 55.0-g piece of copper wire is heated, and the temperature of the wire changes
from 19.0 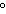 C to 86.0 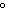 C. The amount
of heat absorbed is 343 cal. What is the specific heat of copper?
|