Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
What is another name for the representative elements?
a. | Group A elements | b. | Group B elements | c. | Group C
elements | d. | transition elements |
|
|
|
2.
|
What is another name for the transition metals?
a. | noble gases | b. | Group A elements | c. | Group B
elements | d. | Group C elements |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following elements is in the same period as phosphorus?
a. | carbon | b. | magnesium | c. | nitrogen | d. | oxygen |
|
|
|
4.
|
Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangement to
predict the properties of missing elements?
a. | Henry Moseley | b. | Antoine Lavoisier | c. | John
Dalton | d. | Dmitri Mendeleev |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following categories includes the majority of the elements?
a. | metalloids | b. | liquids | c. | metals | d. | nonmetals |
|
|
|
6.
|
Of the elements Pt, V, Li, and Kr, which is a nonmetal?
|
|
|
7.
|
In which of the following sets is the symbol of the element, the number of
protons, and the number of electrons given correctly?
a. | In, 49 protons, 49 electrons | b. | Zn, 30 protons, 60
electrons | c. | Cs, 55 protons, 132.9 electrons | d. | F, 19 protons, 19
electrons |
|
|
|
8.
|
The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the
nucleus?
a. | neutrons | b. | protons | c. | electrons | d. | protons and
electrons |
|
|
|
9.
|
What element has the electron configuration 1 s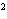 2 s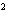 2 p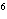 3 s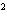 3 p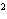 ? a. | nitrogen | b. | selenium | c. | silicon | d. | silver |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following is true about the electron configurations of the noble
gases?
a. | The highest occupied s and p sublevels are completely
filled. | b. | The highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially
filled. | c. | The electrons with the highest energy are in a d sublevel. | d. | The electrons with
the highest energy are in an f sublevel. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following electron configurations is most likely to result in an
element that is relatively inactive?
a. | a half-filled energy sublevel | b. | a filled energy sublevel | c. | one empty and one
filled energy sublevel | d. | a filled highest occupied principal energy
level |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following elements is a transition metal?
a. | cesium | b. | copper | c. | tellurium | d. | tin |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following groupings contains only representative elements?
a. | Cu, Co, Cd | b. | Ni, Fe, Zn | c. | Al, Mg,
Li | d. | Hg, Cr, Ag |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following is true about the electron configurations of the
representative elements?
a. | The highest occupied s and p sublevels are completely
filled. | b. | The highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially
filled. | c. | The electrons with the highest energy are in a d sublevel. | d. | The electrons with
the highest energy are in an f sublevel. |
|
|
|
15.
|
What are the Group 1A and Group 7A elements examples of?
a. | representative elements | b. | transition elements | c. | noble
gases | d. | nonmetallic elements |
|
|
|
16.
|
Of the elements Fe, Hg, U, and Te, which is a representative element?
|
|
|
17.
|
How does atomic radius change from top to bottom in a group in the periodic
table?
a. | It tends to decrease. | b. | It tends to increase. | c. | It first increases,
then decreases. | d. | It first decreases, then increases. |
|
|
|
18.
|
How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic
table?
a. | It tends to decrease. | b. | It tends to increase. | c. | It first increases,
then decreases. | d. | It first decreases, then increases. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Atomic size generally ____.
a. | increases as you move from left to right across a period | b. | decreases as you
move from top to bottom within a group | c. | remains constant within a
period | d. | decreases as you move from left to right across a
period |
|
|
|
20.
|
What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius?
a. | carbon | b. | lithium | c. | potassium | d. | neon |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the increase in atomic size within
a group in the periodic table as the atomic number increases?
a. | an increase in number of occupied energy levels | b. | an increase in size
of the nucleus | c. | an increase in number of protons | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest atomic radius?
a. | chlorine | b. | bromine | c. | sulfur | d. | selenium |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the charge of a cation?
a. | a positive charge | b. | no charge | c. | a negative
charge | d. | The charge depends on the size of the nucleus. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following statements is true about ions?
a. | Cations form when an atom gains electrons. | b. | Cations form when an
atom loses electrons. | c. | Anions form when an atom gains
protons. | d. | Anions form when an atom loses protons. |
|
|
|
25.
|
The metals in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A ____.
a. | gain electrons when they form ions | b. | all form ions with a negative
charge | c. | all have ions with a 1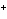 charge charge | d. | lose electrons when
they form ions |
|
|
|
26.
|
Why is the second ionization energy greater than the first ionization
energy?
a. | It is more difficult to remove a second electron from an atom. | b. | The size of atoms
increases down a group. | c. | The size of anions decreases across a
period. | d. | The nuclear attraction from protons in the nucleus
decreases. |
|
|
|
27.
|
In which of the following sets are the charges given correctly for all the
ions?
|
|
|
28.
|
In which of the following groups of ions are the charges all shown
correctly?
|
|
|
29.
|
What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value?
a. | cesium | b. | helium | c. | calcium | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
30.
|
What is the element with the highest electronegativity value?
a. | cesium | b. | helium | c. | calcium | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest ionic radius?
|
|
|
32.
|
For Group 2A metals, which electron is the most difficult to remove?
a. | the first | b. | the second | c. | the
third | d. | All the electrons are equally difficult to remove. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the decrease in ionization energy
within a group in the periodic table as the atomic number increases?
a. | increase in atomic size | b. | increase in size of the
nucleus | c. | increase in number of protons | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest first ionization energy?
a. | sodium | b. | calcium | c. | potassium | d. | magnesium |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following elements has the lowest electronegativity?
a. | lithium | b. | carbon | c. | bromine | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which statement is true about electronegativity?
a. | Electronegativity is the ability of an anion to attract another
anion. | b. | Electronegativity generally increases as you move from top to bottom within a
group. | c. | Electronegativity generally is higher for metals than for
nonmetals. | d. | Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a
period. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion
to its neutral atom?
a. | The radius of an anion is greater than the radius of its neutral
atom. | b. | The radius of an anion is identical to the radius of its neutral
atom. | c. | The radius of a cation is greater than the radius of its neutral
atom. | d. | The radius of a cation is identical to the radius of its neutral
atom. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the increase in ionization energy
from left to right across a period?
a. | an increase in the shielding effect | b. | an increase in the size of the
nucleus | c. | an increase in the number of protons | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level |
|
|
|
39.
|
As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table
____.
a. | ionization energy increases | b. | atomic radii increase | c. | electronegativity
decreases | d. | atomic mass decreases |
|
|
|
40.
|
Of the following elements, which one has the smallest first ionization
energy?
a. | boron | b. | carbon | c. | aluminum | d. | silicon |
|